배추 가격 예측 인공지능 소프트웨어
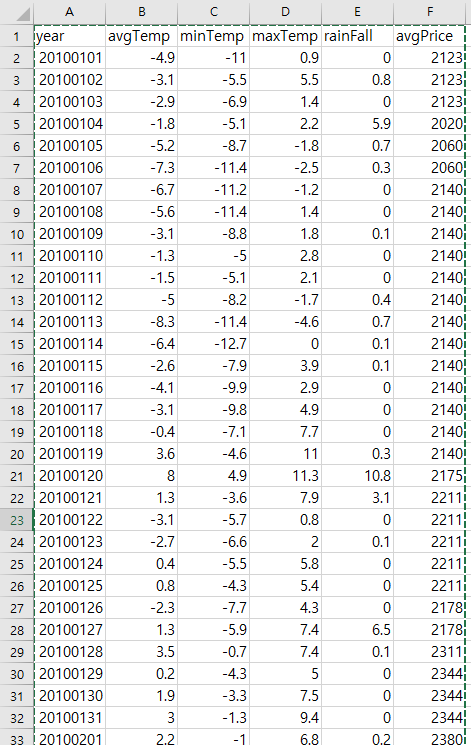
Data
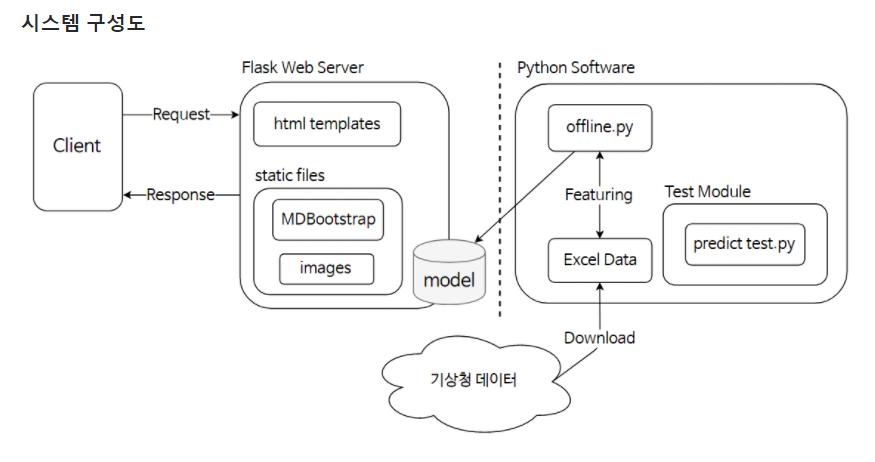
server
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from flask import Flask, render_template, request
import datetime
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
app = Flask(__name__)
# 플레이스 홀더를 설정합니다.
X = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[None, 4])
Y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[None, 1])
W = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([4, 1]), name="weight")
b = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([1]), name="bias")
# 가설을 설정합니다.
hypothesis = tf.matmul(X, W) + b
# 저장된 모델을 불러오는 객체를 선언합니다.
saver = tf.train.Saver()
model = tf.global_variables_initializer()
# 세션 객체를 생성합니다.
sess = tf.Session()
sess.run(model)
# 저장된 모델을 세션에 적용합니다.
save_path = "./model/saved.cpkt"
saver.restore(sess, save_path)
@app.route("/", methods=['GET', 'POST'])
def index():
if request.method == 'GET':
return render_template('index.html')
if request.method == 'POST':
# 파라미터를 전달 받습니다.
avg_temp = float(request.form['avg_temp'])
min_temp = float(request.form['min_temp'])
max_temp = float(request.form['max_temp'])
rain_fall = float(request.form['rain_fall'])
# 배추 가격 변수를 선언합니다.
price = 0
# 입력된 파라미터를 배열 형태로 준비합니다.
data = ((avg_temp, min_temp, max_temp, rain_fall), (0, 0, 0, 0))
arr = np.array(data, dtype=np.float32)
# 입력 값을 토대로 예측 값을 찾아냅니다.
x_data = arr[0:4]
dict = sess.run(hypothesis, feed_dict={X: x_data})
# 결과 배추 가격을 저장합니다.
price = dict[0]
return render_template('index.html', price=price)
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(debug = True)Predict
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
# 플레이스 홀더를 설정합니다.
X = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[None, 4])
Y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[None, 1])
W = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([4, 1]), name="weight")
b = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([1]), name="bias")
# 가설을 설정합니다.
hypothesis = tf.matmul(X, W) + b
# 저장된 모델을 불러오는 객체를 선언합니다.
saver = tf.train.Saver()
model = tf.global_variables_initializer()
# 4가지 변수를 입력 받습니다.
avg_temp = float(input('평균 온도: '))
min_temp = float(input('최저 온도: '))
max_temp = float(input('최고 온도: '))
rain_fall = float(input('강수량: '))
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(model)
save_path = "./saved.cpkt"
saver.restore(sess, save_path)
data = ((avg_temp, min_temp, max_temp, rain_fall), (0, 0, 0, 0))
arr = np.array(data, dtype=np.float32)
x_data = arr[0:4]
dict = sess.run(hypothesis, feed_dict={X: x_data})
print(dict[0])Model
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
from pandas.io.parsers import read_csv
model = tf.global_variables_initializer();
data = read_csv('price data.csv', sep=',')
xy = np.array(data, dtype=np.float32)
# 4개의 변인을 입력을 받습니다.
x_data = xy[:, 1:-1]
# 가격 값을 입력 받습니다.
y_data = xy[:, [-1]]
# 플레이스 홀더를 설정합니다.
X = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[None, 4])
Y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[None, 1])
W = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([4, 1]), name="weight")
b = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([1]), name="bias")
# 가설을 설정합니다.
hypothesis = tf.matmul(X, W) + b
# 비용 함수를 설정합니다.
cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(hypothesis - Y))
# 최적화 함수를 설정합니다.
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate=0.000005)
train = optimizer.minimize(cost)
# 세션을 생성합니다.
sess = tf.Session()
# 글로벌 변수를 초기화합니다.
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
# 학습을 수행합니다.
for step in range(100001):
cost_, hypo_, _ = sess.run([cost, hypothesis, train], feed_dict={X: x_data, Y: y_data})
if step % 500 == 0:
print("#", step, " 손실 비용: ", cost_)
print("- 배추 가격: ", hypo_[0])
# 학습된 모델을 저장합니다.
saver = tf.train.Saver()
save_path = saver.save(sess, "./saved.cpkt")
print('학습된 모델을 저장했습니다.')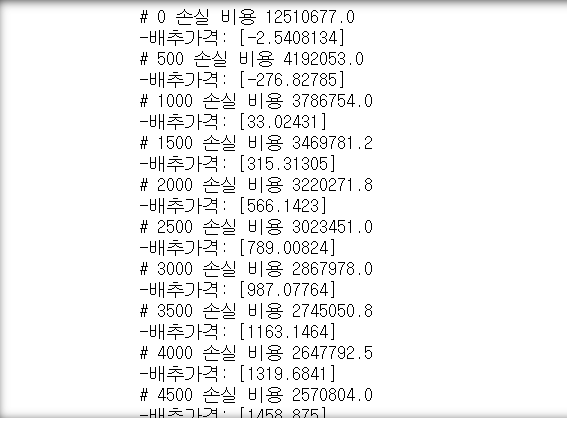
- 연산은 graph로 표현합니다.
- graph는 Session내에서 실행됩니다.
- 데이터는 tensor로 표현합니다.
- 변수(Variable)는 그 상태를 유지합니다.
- 작업(operation 혹은 op)에서 데이터를 입출력 할 때 feed와 fetch를 사용할 수 있습니다.
1. 그래프(Graph)
노드(node)와 꼭짓점(vertex)으로 연결되어 있는 객체이다. 노드들은 변(edge)를 통해 연결되어 있다.
문서에 나와있는 그래프라는 표현이 어렵다면, 쉽게 이해하기 위해서 그래프라고 나와있는 부분에 '연산'이라는 용어를 대체해서 넣어보면 이해를 하기 쉽다.
(연산을 operation 혹은 op라고 부른다.)
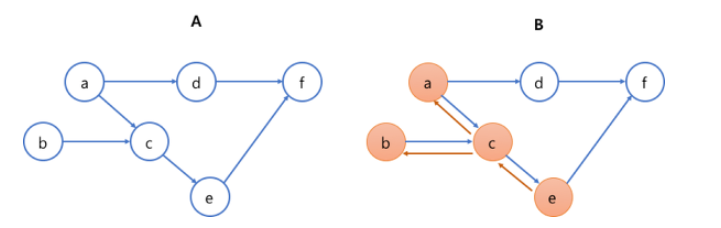
왜 텐서플로우에서는 그래프를 사용하는가?
이미지를 보면 우리가 e를 구하기 위해서 모든 것을 다 계산 할 필요 없이
a,b,c를 계산하면 e를 구할 수 있다.
이런 방식으로 연산에 필요한 것들을 분별할 수 있는 구조가 그래프이다.
결국 목적은 불필요한 연산을 조금이라도 줄이기 위해서이다.
2. 텐서(Tensor)
다차원 배열 혹은 다차원 리스트라고 생각을 하면 된다.
텐서플로우의 모든 데이터들의 종류(플레이스홀더, 상수, 변수)는 텐서이다.
변수, 상수와 텐서의 개념이 헷갈릴 수도 있다.
여기에서 변수, 상수는 우리가 연산하는 과정에서, 각자 맡는 역할에 대한 용어이고
그 모든 데이터들의 타입(종류)이 텐서라는 것이다.
3. 상수(constant)
tf.constant(value, dtype=None, shape=None, name='Const')
의 형태로 표현을 한다.
일반적인 프로그래밍에서의 상수 의미와 동일하다.
4. 변수(variable)
예를들어, 가중치 식을 y = W*x + b 라고 보는데,
입력값 x를 넣어서 해당 y값을 맞춰줄수 있는 W와 b를 구하는 것이 머신러닝이다.
이때, 텐서플로우에서는 W와 b를 변수로 만들어서 구하는 것이다.
모델을 학습을 시킬때, 최종 값을 얻기 위해 계속 수정해야하는 값들을 변수로 두는 것이라고 생각하면 된다.
5. 세션 (Session)
텐서플로우 작동 방식을 2가지 과정으로 나타내면,
① 모든 것을 파이썬에서 디자인(설계)을 한 후
② 외부에서 연산을 돌린다
②에서 연산을 실행시키는 곳이 Session
구체적으로 device(CPUs, GPUs) 위에서 연산을 실행하는 것이다.
세션은 텐서플로우 계산이 돌아갈 수 있는 환경을 만들어주는 코드라고 보면 된다.
"스마트인재개발원에서 진행된 수업내용입니다"
스마트인재개발원
4차산업혁명시대를 선도하는 빅데이터, 인공지능, 사물인터넷 전문 '0원' 취업연계교육기관
www.smhrd.or.kr
'스마트 인재개발원 > 2차프로젝트' 카테고리의 다른 글
| (광주인공지능학원) 2차프로젝트 마무리 및 다니면서 느낀점 (4) | 2021.07.17 |
|---|---|
| (스마트인재개발원) 2차프로젝트 머신러닝 마무리 (0) | 2021.07.17 |
| (스마트인재개발원) 2차프로젝트 데이터 전처리 2차 (모델재선택) (0) | 2021.07.05 |
| (스마트인재개발원) 프로젝트 기획 발표 (1) | 2021.07.04 |
| (스마트인재개발원) 2차프로젝트 데이터 전처리 (0) | 2021.07.04 |